Soya has sparked widespread debate in health and nutrition circles — some praise it as a nutritional powerhouse, while others question its safety.
MICROBIOMES4SOY partner, The European Food Information Council (EUFIC) wrote an article entitled “Is Soy Good or Bad for You? Here’s What the Science Says”, providing an in-depth, evidence-based exploration of soya’s role in human health, complementing the research focus of Microbiomes4Soy.
📢 Read the full EUFIC article here: Is Soy Good or Bad for You? Here’s What the Science Says.
The MICROBIOMES4SOY project explores how beneficial microbes can enhance soya’s performance, making it more resilient in agriculture, optimising aquaculture feeds, and improving the health benefits of soya-based diets. Through our research, we aim to unlock the full potential of soya, contributing to more sustainable food systems.
Stay tuned for more updates from MICROBIOMES4SOY as we continue advancing sustainable food solutions.
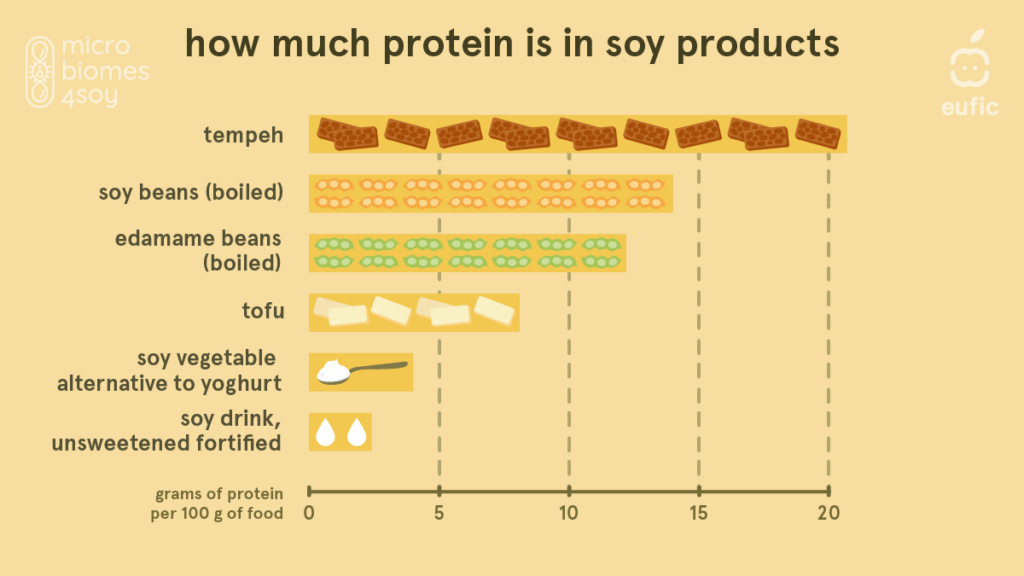
Soy contains a wide range of nutrients, including as a source of high-quality protein that is well-digested. Soy also contains all nine essential amino acids in consistent amounts. The image below shows the protein content in various soya products.